Water is a necessary component in the operation of our facilities and an indispensable part of the daily life of our communities. Therefore, it’s critical to manage the resource carefully for our communities and operations, as well as for the future generations.



Although our operations are not as water intensive as manufacturing, water is essential to our operations and we consider it as a material aspect. We use water mainly for our office and catering facilities or in HVAC to support the cooling equipment. Since most of our international operations facilities are on leases or are located in regions that are abundant in water supply, we consider water as a material issue for our Indian operations only. We are working on the responsible sourcing practices to be incorporated with our overall water management strategy. During the reporting period, we withdrew (including requirement for our customers) nearly 640,348 kl of water of which 91% was from municipal facilities, 8% from third-party tankers and bottled water, and the remaining 1% was accessed from rainwater harvesting and ground water. Water recycling accounts for 8% of the total water withdrawal. In smaller sites where recycling and treating installation is not feasible, the wastewater is discharged into the municipal drainage system after appropriate approvals from the authorities.
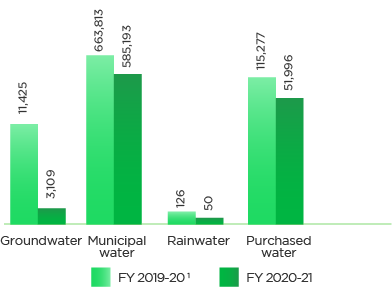
1 Restatement - In FY 2019-20, the reported total water withdrawal was 4.62 lakh kl. However, the actual water withdrawal was 790,641 kl. The difference in figures is due to faulty meters by local authorities in two facilities which now have been replaced with new accurate ones and the values have accordingly been adjusted.
The above data includes customer requirements as well.
Water risk assessment
We conduct water risk assessment periodically to map the impact of water consumption in our direct operations. This year, we revisited the assessment exercise for all major facilities with the objective of identifying the consumption pattern, water related risk and opportunities (current and future) within the Indian facilities. The assessment results showed that most of the facilities were in the medium and low risk categories. However, for facilities mainly in southern region of India such as in Ambattur and VSB Chennai, risk factors such as drought conditions, inadequate municipal and private infrastructure could have extremely high impact on business continuity as witnessed in the past. In Delhi, the decreasing water surface level is a concern. Based on the assessment results, a few recommendations were proposed to reduce the impact of risk factors. These recommendations are being worked on and will be implemented by FY 2021-22.
Water management strategy
Keeping 3R’s (Reduce, Reuse and Recycle) as a core strategy, we are committed to reducing our water footprint throughout our operations by optimising water consumption and increasing our recycling capacity
Consumption, monitoring and awareness
Resource allocation
Minimising waste
19%
Water savings in FY 2020-21 in comparison with FY 2019-20 including water supplied to customers.
Reduce
We optimise the use of water in our facilities primarily through technological interventions. Keeping track of water usage with the latest and innovative technology and equipment maximises water savings significantly. We have installed sensor-based water taps at all restrooms and cafeteria in our major locations to reduce water consumption.
To further account for our consumption at each activity level, we are automating and increasing water meter installations at all our facilities. Following the success of the pilot IoT water monitoring project at the Dighi campus, Pune, we are installing IoT meters in the rest of our major facilities. The project will be implemented in FY 2021-22. The project is expected to strengthen the monitoring of water loss and help in substantial water savings in the facilities.
Reuse
We utilise water treated at our sewage treatment plant with nearly 50,175 kl volume for processes such as landscaping and gardening. This has not only resulted in cost savings but also minimised the freshwater withdrawal to conduct such activities.
To maximise the rainwater harvesting capacity, we have conducted feasibility studies at six of our sites. Based on the results of the studies, we will increase our rainwater harvesting capability beginning FY 2021-22. The total rainwater harvesting capacity is expected to be 5,886 kl once the project has been implemented at the identified sites
Recycle
In a water-stressed country like India, the recycling and efficient use of water is crucial. We have, thus, installed wastewater treatment plants at most of our facilities. During FY 2020‑21, we recycled nearly 50,175 kl of water back into gainful use, totally nearly 8% of our total water requirement.
50,175 kl
Water recycled back into gainful use

Cooling the soil through drip irrigation

Being one of the largest facilities with sprawling green spaces, Dighi, Pune renewed and rejuvenated its drip irrigation system. The key objective of the initiative is to ensure that the soil has enough moisture essential for plant growth, and the surrounding atmosphere is suitable for plant growth. Through this irrigation method, water and nutrients are delivered directly to plant roots.
Benefits
We make focused efforts within the boundary of our operations to facilitate proper waste segregation and resource conservation by minimising waste generation.



Our waste management system includes waste segregation at source and disposal as per waste categorisation. We also practise efficient and environment-friendly end-of-life disposal methods to ensure that the impact of the waste generated is minimum. We also reduce waste that enters landfills.
Being a service-oriented company, we do not generate process and manufacturing waste. The products and service inputs we receive from our suppliers to support our operations are essentially based on business requirement. Therefore, we have minimal control over it. For our own operations, we are committed to reducing waste and expanding our recycling options wherever feasible. On the customer side, due to the nature of the business, waste generation is negligible since there is no tangible products being manufactured.
Waste footprint
In our operations, we categorise waste as non-hazardous and hazardous waste. Nonhazardous waste mainly consists of municipal solid waste (paper, food, dry leaves, cartons, plastic and others) generated and can be easily recycled. Hazardous waste is generated mainly from the high-end equipment which are required to operate our facilities and require authorised treatment procedures.
For both types of waste, recycling and disposal is done through authorised vendors.
Non-hazardous waste
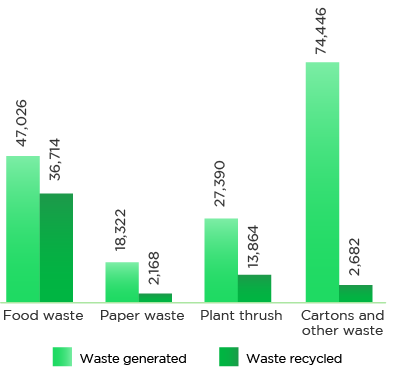
We dispose the non-hazardous waste generated at our facilities through various channels such as recyclers and the municipal corporation. For paper waste generated in the form of newspapers, printed papers, and cartons, we have tied up with various NGOs such as Green Yatra, that work towards recycling of waste while providing livelihoods. We have sent ~2,168 kgs of paper waste for recycling.
Organic Waste Convertors (OWC) have been installed at all our major facilities to convert the food waste generated from our cafeterias into manure and reuse it within the facilities.
36,714 kgs
Food waste composted in-house
Our Corporate Services team organises regular awareness sessions for waste handlers within the facility to ensure proper waste management.

Banning single-use plastic

We implemented the ban on the use of plastic products in our pan-India offices to ensure zero plastic waste in our premises. We discontinued the use of plastic wraps to cover sterilised glass tumblers, and stopped using food grade PET water bottles, plastic coasters and other goods. We also initiated replacement of PVC waste bins with stainless steel ones, PVC indoor flowerpots with terracotta or equivalent products. To create awareness about the implementation, posters were displayed in the offices.
Impact
Hazardous waste
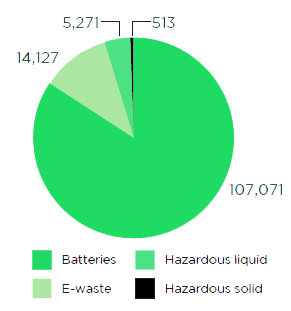
Hazardous waste such as used oil, oil filter and oil-soaked cotton from DG sets, used batteries from energy utilities, and e-waste is generated from equipment such as desktop, laptops and other office and IT equipment. We ensure adequate storage with secondary containment during the collection and handling of such hazardous waste, and proper training for the waste handlers. We ensure that 100% of this waste is sent to authorised recyclers and processors through Metal Scrap Trade Corporation Limited and we ensure that all regulatory requirements of waste management and rules of regions or countries are followed in the process.
Hazardous waste generated (kgs)
Diesel spill incident

Name of TC entity-Tata Communications International Pte Ltd. / Laurentide Facility, Canada: As the delivery truck was emptying 16,000 litres of diesel fuel at the facility the low temperature conditions and accumulation of ice in the vent pipe caused high pressure to build up, preventing the free flow of 100 litres of diesel fuel in the immediate environment.
Remedial and corrective action: Although the incident was small and localised, it still got reported to the local authorities. Within few hours of the incident, a specialised environmetal team removed the contaminated snow and soil from the location. Soil samples at various depths of the ground were collected and sent for further investigation. As for the source of the spill, ice build-up in the vent was removed along with raising the vent height by about 2 meters above the roof line to prevent a similar situation to reproduce again. Final reports are awaited which would confirm that the clean-up is effective and complete. The learnings from this step will help in developing more goals to strengthen the sustainability vision of the Company.
Business impact: We await reports from the insurance company, whether Tata Communications is liable for the remediation cost or the fuel delivery company is responsible for the remediation cost.
COVID-19 related waste disposal implementation

With the spread of COVID-19, it became imperative to arrange for the safe disposal of COVID-19 related waste such as PPE kits as per government guidelines in our pan India offices. This was necessary to ensure the safety of the workplace and the containment of the disease. It was also important to create awareness among internal and external stakeholders on the importance of safe disposal. Yellow bins were installed to collect such waste. We also implemented a process to store the collected waste in an enclosed area for 72 hours and subsequently cut/shred the waste in order to make it unfit for reuse. Stickers were pasted on foot-operated yellow bins marking them out for the disposal of bio-medical waste. Awareness was created amongst employees via virtual connect on the disposal process.
Impact